The Chinese search engine market presents unique challenges and opportunities for businesses seeking visibility online. For many international firms, especially B2B organizations, partnering with a B2B Baidu SEO agency is a practical way to bridge cultural, technical, and regulatory gaps. Understanding the fundamental differences between Baidu SEO and Google SEO across multiple optimization dimensions is crucial for success in both markets. This analysis examines these differences through four key perspectives: on-site SEO, off-site SEO, technical SEO, and generative engine optimization.
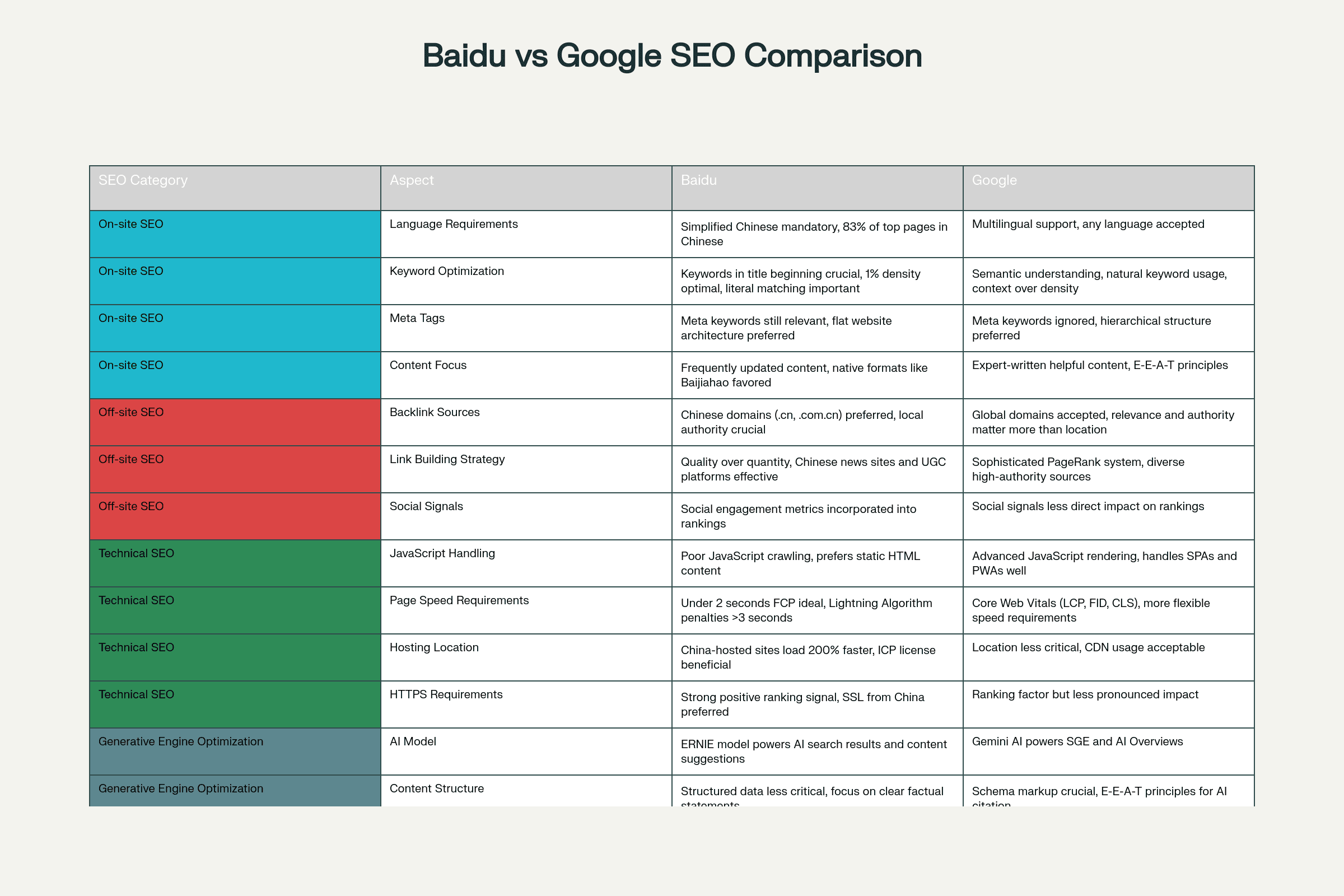
Comprehensive comparison of Baidu vs Google SEO differences across on-site, off-site, technical, and generative engine optimization categories.
On-Site SEO Differences
1. Language and Content Requirements
Baidu maintains strict language preferences that significantly impact rankings. Over 83% of Baidu's top-ranking pages are written in Simplified Chinese, making native Chinese content non-negotiable for serious market penetration. This requirement is particularly relevant to B2B sites and the work of a B2B Baidu SEO agency. Content must feel natural to native readers rather than simply translated. In contrast, Google embraces multilingual diversity, effectively indexing and ranking content in any language with equal algorithmic consideration.
Baidu's algorithm favors literal keyword matching more heavily than Google's semantic approach. For Baidu optimization, placing target keywords at the beginning of title tags shows strong correlation with higher rankings, while maintaining approximately 1% keyword density across content.Experienced B2B Baidu SEO agency practitioners understand how to balance literal matching with readability. Google has evolved beyond this approach, prioritizing semantic understanding and natural language patterns over rigid keyword density formulas.
2. Meta Tags and Site Architecture
A significant technical difference lies in Baidu's continued reliance on traditional SEO signals that Google has largely deprecated. Baidu still uses meta keyword tags and flat website architecture as ranking signals, requiring SEO practitioners to revisit "old-school" tactics when optimizing for the Chinese market. A competent B2B Baidu SEO agency will adapt these tactics into a modern optimization plan.Google has moved away from these signals, favoring hierarchical site structures and ignoring meta keyword tags entirely.
3. Content Strategy Focus
Baidu prioritizes frequently updated content and shows preference for native formats such as Baijiahao articles. The platform emphasizes site structure, internal linking, and user engagement metrics more than backlink authority. A well-structured content calendar designed by a B2B Baidu SEO agency can help sustain the frequent updates Baidu rewards. Google has shifted toward expert-written, helpful content following E-E-A-T principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), with particular emphasis on people-first content that aligns with user intent.[5][3]
Off-Site SEO Strategies
1. Backlink Source Preferences
Baidu demonstrates strong geographic bias in link evaluation, valuing backlinks from Chinese-based websites, especially those with .cn or .com.cn domains. Links from websites with ICP (Internet Content Provider) licenses and verified physical addresses in China carry significantly more weight. This creates substantial barriers for international businesses without local presence.
Google employs a more sophisticated, location-agnostic approach through its PageRank system, evaluating backlinks based on relevance and authority of the linking site regardless of geographic location. This global perspective allows businesses to build authority through diverse, high-quality international link sources.
2. Link Building Methodology
The Chinese internet landscape features fewer privately run websites, requiring more targeted link building approaches for Baidu. Effective strategies include focusing on Chinese-language websites from Singapore, Hong Kong, and Taiwan, leveraging User Generated Content (UGC) platforms like Baidu Tieba and Zhihu, and publishing on Chinese news websites.
Baidu is more vulnerable to link spam manipulation but imposes heavy penalties when detected, with recovery sometimes taking years. Recent Moneyplant Updates have specifically targeted spammy link-building techniques, shifting emphasis toward quality over quantity.
3. Social Signal Integration
Baidu uniquely incorporates social signals into its ranking algorithm, unlike Google where social signals have less direct impact. Likes, shares, and user-generated content can positively impact organic visibility on Baidu, especially for e-commerce sites. This integration reflects the social nature of Chinese internet culture and platforms.
Technical SEO Requirements
1. JavaScript and Modern Web Technologies
A critical technical difference lies in crawling capabilities. Baidu struggles significantly with JavaScript and AJAX crawling, making content hidden behind client-side rendering potentially invisible to Baidu's indexing system. Important content should be fully visible in raw HTML for optimal Baidu performance.
Google effectively handles modern web technologies, including Single Page Applications (SPAs) and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), allowing for more dynamic website architectures without SEO penalties.
2. Page Speed and Performance
Baidu maintains stricter page speed requirements with ideal load times under 2 seconds for First Contentful Paint (FCP). The Lightning Algorithm specifically rewards mobile pages loading within two seconds while penalizing those exceeding three seconds. Sites hosted in China experience loading advantages of up to 200% faster than international hosting.
Google uses Core Web Vitals (Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, Cumulative Layout Shift) with more flexible standards, stating that "a slow page may still rank highly if it has great, relevant content".
3. Security and Hosting Considerations
HTTPS serves as a stronger positive ranking signal for Baidu, with SSL certificates purchased from within China preferred. The ICP license requirement creates additional compliance hurdles for international businesses, as sites without proper licensing face visibility limitations regardless of optimization quality.
Google treats HTTPS as a ranking factor but with less pronounced impact compared to Baidu's emphasis on security and local compliance.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
1. AI Model Differences
Baidu employs its ERNIE model (Enhanced Representation through kNowledge IntEgration) to power AI-driven search results and content suggestions. ERNIE uses deep learning to analyze data patterns and create optimized content recommendations, with particular strength in understanding Chinese language context and cultural nuances.
Google's Gemini AI powers Search Generative Experience (SGE) and AI Overviews, focusing on conversational query understanding and multi-step question optimization. Gemini's global training allows for more diverse language and cultural context understanding.
2. Content Optimization for AI
Traditional keyword signals remain more important for Baidu's AI understanding, as ERNIE still relies heavily on literal on-page signals and identifiable patterns. Clear keyword integration in titles, headings, and opening paragraphs directly influences ERNIE's content evaluation.
Google's GEO strategy requires response-oriented writing, emphasizing content that directly answers natural questions within the first three sentences of each section. Schema markup and structured data become crucial for Google's AI systems to understand and cite content accurately.
3. Citation and Visibility Strategies
Baidu's generative approach continues to favor structured, frequently updated content with clear factual statements. The platform's ecosystem integration with properties like Baidu Baike and Baidu Tieba provides additional optimization opportunities.
Google's GEO focuses on conversational queries and comprehensive coverage, requiring optimization for featured snippets and voice search results. E-E-A-T principles become even more critical for AI citation, with emphasis on expertise demonstration and authoritative source establishment.
Strategic Implications for Baidu SEO Agencies and B2B Marketing
1. Agency Specialization Requirements
Baidu SEO agencies must navigate significantly more complex regulatory and cultural landscapes. Successful agencies emphasize localized expertise, including understanding of ICP licensing requirements, cultural content adaptation, and Baidu's unique algorithm preferences. The need for native Chinese speakers and cultural understanding makes specialized agency partnerships often essential for international businesses.
2. B2B Baidu Marketing Considerations
B2B companies face unique challenges in the Chinese digital ecosystem. Baidu SEM and SEO for B2B success requires understanding of longer sales cycles, relationship-building culture, and industry-specific content needs. B2B marketers can leverage Baidu's advanced audience targeting options through industry, location, and company size parameters.
3. B2B content strategies must focus on thought leadership and educational content to establish industry authority. Integration with platforms like Baidu Zhidao (Q&A platform) and Baidu Tieba forums provides community engagement opportunities crucial for B2B relationship building.
The strategic complexity of Baidu optimization, combined with regulatory requirements and cultural considerations, makes specialized Baidu SEO agency partnerships particularly valuable for international B2B companies seeking sustainable growth in the Chinese market.
Conclusion
The fundamental differences between Baidu and Google SEO extend far beyond simple algorithmic variations. Baidu's approach reflects the unique characteristics of the Chinese internet ecosystem, including regulatory requirements, cultural preferences, and technical infrastructure limitations. Success in Chinese search requires dedicated strategies that cannot simply be adapted from Google SEO practices.
For businesses serious about Chinese market penetration, understanding these differences across on-site optimization, off-site authority building, technical requirements, and emerging generative AI optimization is essential. The complexity and specialization required often necessitate partnerships with experienced Baidu SEO agencies who understand both the technical and cultural nuances of this critical market. Below is a GEO-ready FAQ set (prompt-shaped questions, direct answers, no filler) derived from your “Baidu vs Google SEO” article.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
On-page SEO FAQs
What language should I publish in for Baidu SEO versus Google SEO?
For Baidu SEO, Simplified Chinese content is non-negotiable because the majority of top-ranking Baidu pages are written in Simplified Chinese.
Google can index and rank content in many languages without the same single-language preference.
How does keyword usage differ between Baidu SEO and Google SEO?
Baidu favors literal keyword matching more than Google’s semantic approach.
For Baidu, placing target keywords at the beginning of title tags and maintaining roughly 1% keyword density is described as correlating with better rankings, while Google prioritizes natural language patterns over rigid density rules.
Do meta keywords matter for Baidu, and do they matter for Google?
Baidu still uses meta keyword tags as a ranking signal, so “old-school” meta keyword optimization remains relevant.
Google ignores meta keyword tags and instead favors modern site structures and other signals.
How should content strategy differ for Baidu versus Google?
Baidu prioritizes frequently updated content and prefers native ecosystem formats such as Baijiahao articles.
Google emphasizes expert-written, helpful content aligned with E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) and people-first intent matching.
Off-page SEO FAQs
What kinds of backlinks does Baidu value versus Google?
Baidu shows geographic bias and values backlinks from Chinese-based websites, especially .cn or .com.cn domains.
Google evaluates backlinks more location-agnostically, emphasizing relevance and authority of the linking site regardless of geography.
Why does an ICP license matter for Baidu SEO?
Baidu gives more weight to links from sites with ICP licenses and verified physical addresses in China, which creates a barrier for international businesses without local presence.
The ICP requirement also creates compliance hurdles that can limit visibility regardless of optimization quality.
What link-building methods work better in China’s web ecosystem?
The Chinese internet has fewer privately run websites, so Baidu link building often relies more on targeted placements and platforms.
The article highlights Chinese-language sites in Singapore/Hong Kong/Taiwan, UGC platforms like Baidu Tieba and Zhihu, and Chinese news sites as practical channels.
How do Baidu and Google differ on social signals?
Baidu incorporates social signals into rankings more directly, so likes, shares, and UGC can lift organic visibility.
Google is described as having less direct ranking impact from social signals.
Technical SEO FAQs
Can Baidu crawl JavaScript websites as well as Google?
Baidu struggles with JavaScript and AJAX crawling, so content behind client-side rendering can be missed or not indexed properly.
Google crawls modern web tech more effectively, including SPAs and PWAs, which enables more dynamic architectures without the same crawl limitations.
What page-speed targets matter for Baidu versus Google?
Baidu has stricter speed expectations, with an ideal First Contentful Paint under 2 seconds and a Lightning Algorithm that rewards mobile pages loading within two seconds while penalizing those over three seconds.
Google uses Core Web Vitals but is described as more flexible, noting a slow page can still rank if content is highly relevant.
Does hosting location affect Baidu performance?
Hosting in China can create major speed advantages, with the article stating sites hosted in China can load up to 200% faster than international hosting.
Because Baidu speed thresholds are strict, this performance gap becomes a direct ranking lever rather than a minor technical detail.
Is HTTPS more important for Baidu than Google?
HTTPS is presented as a stronger positive ranking signal for Baidu, with a preference for SSL certificates purchased within China.
Google also treats HTTPS as a ranking factor, but with less pronounced impact compared with Baidu’s security and local compliance emphasis.
GEO (Generative Search) FAQs
What AI models power Baidu and Google’s generative experiences?
Baidu uses ERNIE to power AI-driven search results and content suggestions, with strength in Chinese language context and cultural nuance.
Google uses Gemini for SGE and AI Overviews, focusing on conversational query understanding and multi-step question handling.
How should GEO writing differ for Baidu versus Google?
For Baidu, traditional keyword signals remain more important for AI understanding, so clear keyword placement in titles, headings, and opening paragraphs is emphasized.
For Google, the article states GEO should be response-oriented, directly answering natural questions early and using structured data so systems can understand and cite content.
Should I add FAQ structured data for this article?
FAQPage structured data is eligible for FAQ rich results only for well-known, authoritative government-focused or health-focused sites, but the markup still helps machines interpret Q&A structure.
If you use it, ensure each question has a single accepted answer and the FAQ content is visible on the page (answers can be in expandable sections if users can open them).
